In reversing the first K elements of a queue problem we have given a queue and a number k, reverse the first k elements of a queue using standard operations of the queue.
Table of Contents
Examples
Input:
queue = 10 -> 15 -> 31 -> 17 -> 12 -> 19 -> 2
k = 3
Output:
queue = 31 -> 15 -> 10 -> 17 -> 12 -> 19 -> 2
Input:
queue = 12 -> 14 -> 16 -> 7 -> 9
k = 2
Output:
queue = 14 -> 12 -> 16 -> 7 -> 9
Algorithm for Reversing the First K elements of a Queue
To reverse the first k elements of the queue we can use a stack.
- Remove first k elements of the queue and push them into a stack.
- Pop all the elements of the stack and push them to the end of the queue.
- Pop-out (n – k) elements from the front of the queue and push them to the end of the queue, where n is the total number of elements in the queue.
- First, k elements of the queue are reversed, print the elements of the queue.
Explanation for Reversing the First K elements of a Queue
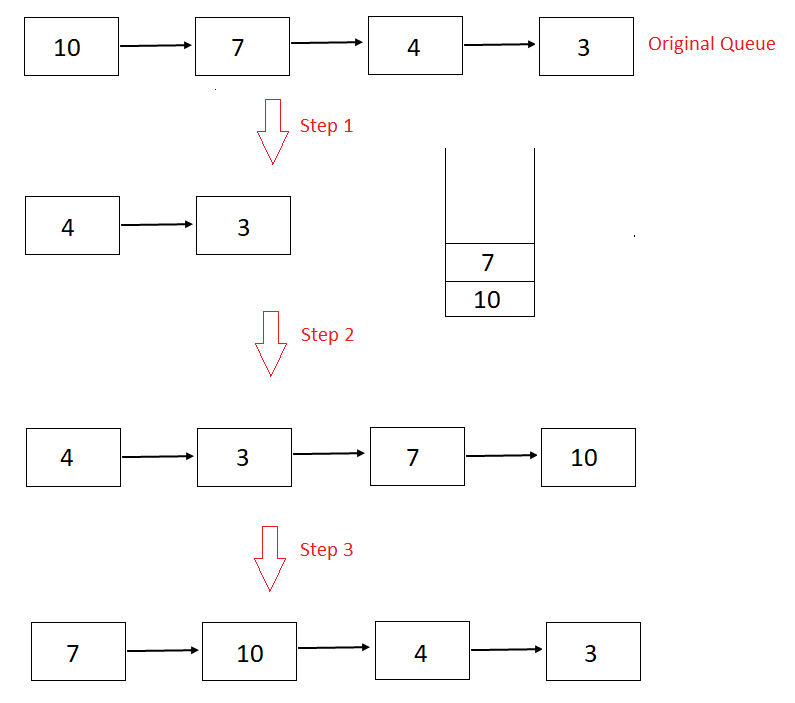
Consider an example,
queue = 10 -> 7 -> 4 -> 3
k = 2
Step 1
Remove first k elements of the queue and push them into a stack.
queue = 10 -> 7 -> 4 -> 3 and stack = null
Iteration 1
queue = 7 -> 4 -> 3 and stack = 10
Iteration 2
queue = 4 -> 3 and stack= 7 -> 10
Step 2
Pop all the elements of the stack and push them to the end of the queue.
queue= 4 -> 3 and stack= 7 -> 10
Iteration 1
queue= 4 -> 3 -> 7 and stack = 10
Iteration 2
queue = 4 -> 3 -> 7 -> 10 and stack = null
Step 3
Pop out (n – k) elements from the front of the queue and push them to the end of the queue
queue = 4 -> 3 -> 7 -> 10
Iteration 1
queue = 3 -> 7 -> 10 -> 4
Iteration 2
queue = 7 -> 10 -> 4 -> 3
JAVA Code
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class ReversingTheFirstKElementsOfAQueue {
private static void reverseKElements(Queue<Integer> queue, int k) {
if (k < 0 || k >= queue.size() || queue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Invalid Input");
return;
}
int n = queue.size();
// remove first k elements of queue and push in stack
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int curr = queue.poll();
stack.push(curr);
}
// Pop out elements from stack and add to the end of the queue
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int curr = stack.pop();
queue.add(curr);
}
// Remove first (n - k) elements of the queue and add them to the end
for (int i = 0; i < n - k; i++) {
int curr = queue.poll();
queue.add(curr);
}
// Print the elements of the queue
for (Integer i : queue) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example 1
Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<>();
int k1 = 3;
q1.add(10);
q1.add(15);
q1.add(31);
q1.add(17);
q1.add(12);
q1.add(19);
q1.add(2);
reverseKElements(q1, k1);
// Example 2
Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<>();
int k2 = 2;
q2.add(12);
q2.add(14);
q2.add(16);
q2.add(7);
q2.add(9);
reverseKElements(q2, k2);
}
}31 15 10 17 12 19 2 14 12 16 7 9
C++ Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void reverseKElements(queue<int> &queue, int k) {
if (k < 0 || k >= queue.size() || queue.empty()) {
cout<<"Invalid Input"<<endl;
return;
}
int n = queue.size();
// remove first k elements of queue and push in stack
stack<int> st;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int curr = queue.front();
queue.pop();
st.push(curr);
}
// Pop out elements from stack and add to the end of the queue
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int curr = st.top();
st.pop();
queue.push(curr);
}
// Remove first (n - k) elements of the queue and add them to the end
for (int i = 0; i < n - k; i++) {
int curr = queue.front();
queue.pop();
queue.push(curr);
}
// Print the elements of the queue
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int curr = queue.front();
queue.pop();
cout<<curr<<" ";
queue.push(curr);
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
// Example 1
queue<int> q1;
int k1 = 3;
q1.push(10);
q1.push(15);
q1.push(31);
q1.push(17);
q1.push(12);
q1.push(19);
q1.push(2);
reverseKElements(q1, k1);
// Example 2
queue<int> q2;
int k2 = 2;
q2.push(12);
q2.push(14);
q2.push(16);
q2.push(7);
q2.push(9);
reverseKElements(q2, k2);
}31 15 10 17 12 19 2 14 12 16 7 9
Complexity Analysis for Reversing the First K elements of a Queue
Time Complexity = O(n + k)
Space Complexity = O(k)
where n is the number of elements in the queue.