Table of Contents
Problem Statement
Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal LeetCode Solution – Given the root of a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
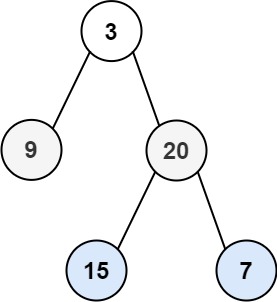
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
Explanation
We carry out simple level-order traversal but reverse alternate levels before adding them to the ans.
In this problem, we need to traverse the binary tree level by level. When we see levels in a binary tree, we need to think about BFS, because it is its logic: it first traverses all neighbors, before we go deeper. Here we also need to change direction on each level as well. So, the algorithm is the following:
- We create a queue, where we first put our root.
resultis to keep the final result anddirection, equal to1or-1or we can keep it as a boolean in the direction of traverse.- Then we start to traverse level by level: if we have
kelements in queue currently, we remove them all and put their children instead. We continue to do this until our queue is empty. Meanwhile, we formlevellist and then add it toresult, using correct direction and changing direction after.
Code
C++ Code for Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return vector<vector<int> > ();
}
vector<vector<int> > result;
queue<TreeNode*> nodesQueue;
nodesQueue.push(root);
bool leftToRight = true;
while ( !nodesQueue.empty()) {
int size = nodesQueue.size();
vector<int> row(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = nodesQueue.front();
nodesQueue.pop();
// find position to fill node's value
int index = (leftToRight) ? i : (size - 1 - i);
row[index] = node->val;
if (node->left) {
nodesQueue.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
nodesQueue.push(node->right);
}
}
// after this level
leftToRight = !leftToRight;
result.push_back(row);
}
return result;
}
};Java Code for Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root)
{
List<List<Integer>> sol = new ArrayList<>();
travel(root, sol, 0);
return sol;
}
private void travel(TreeNode curr, List<List<Integer>> sol, int level)
{
if(curr == null) return;
if(sol.size() <= level)
{
List<Integer> newLevel = new LinkedList<>();
sol.add(newLevel);
}
List<Integer> collection = sol.get(level);
if(level % 2 == 0) collection.add(curr.val);
else collection.add(0, curr.val);
travel(curr.left, sol, level + 1);
travel(curr.right, sol, level + 1);
}
}Python Code for Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
class Solution:
def zigzagLevelOrder(self, root):
if not root: return []
queue = deque([root])
result, direction = [], 1
while queue:
level = []
for i in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
level.append(node.val)
if node.left: queue.append(node.left)
if node.right: queue.append(node.right)
result.append(level[::direction])
direction *= (-1)
return resultComplexity Analysis for Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal LeetCode Solution
Time Complexity
O(N)
Space Complexity
O(N)